|
The existing regulatory framework and growing transparency requirements around fintech adoption and digital asset holdings in Saudi Arabia create a foundation for our analysis this week to explore the inclusion of Bitcoin in particular as a collateral on corporate balance sheets. This means that holders of Bitcoin can leverage their digital assets to obtain loans and raise capital without having to sell their what’s known as the ‘digital gold’, potentially benefiting from its future price appreciation. Instead, they pledge their Bitcoin as security (collateral) to lenders. Another factor supporting the consideration of Bitcoin as collateral is the growing trading volume on offshore exchanges and peer-to-peer platforms, fueled by a young, tech-savvy population and the widespread adoption of mobile banking. Regulatory sandboxes in the kingdom could allow financial institutions and fintech companies to experiment with the use of Bitcoin in secured lending. This controlled setting will provide insightful data to policy makers into market acceptance, liquidity effects, and potential operational challenges, as well as allowing the financial sector to innovate responsibly. The Saudi fintech landscape including the use of blockchain – which enables secure, transparent, and tamper-proof recording of transactions -- has expanded significantly in recent years, with the number of fintech companies growing from fewer than 20 in 2018 to over 200 by 2024. There is no official data available regarding the revenue of the cryptocurrencies market in the Kingdom; however, some projections estimate that it could reach approximately US$769 2M by the end of 2025. When comparing globally, the highest revenue is achieved in the United States, reaching US$ 16.1bn in 2025. This vast difference highlights the relative maturity and scale of the US crypto ecosystem. Two US presidential executive orders have marked this crytpo development. The first aims to deregulate the industry and facilitate U.S. leadership in the crypto space. The second has established a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve to stockpile Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, positioning them as a new class of sovereign national asset. 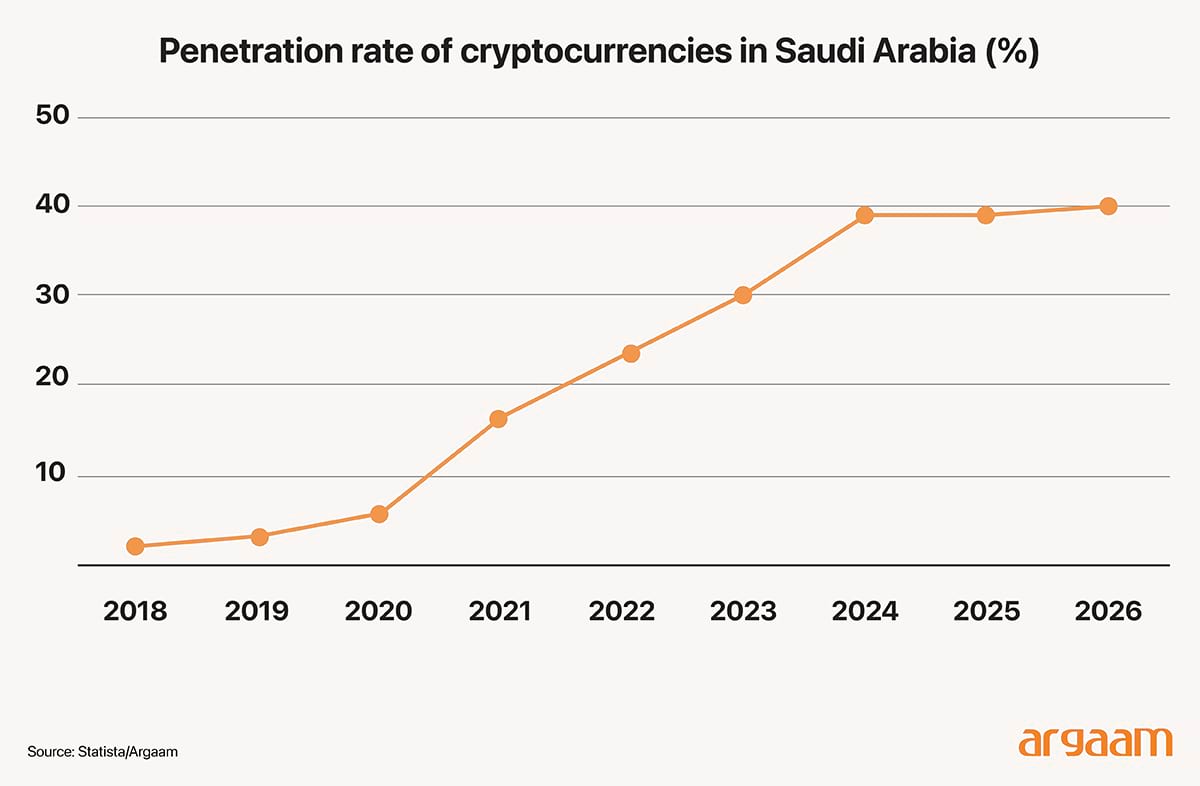 
Bitcoin on the Balance Sheet
Typically, Bitcoin is classified as an intangible asset or, in some cases, as inventory or an investment asset in a company’s balance sheet, depending on the company’s business model. A company that acquires Bitcoin to hold as a long-term investment, for example, would report it as intangible assets with indefinite useful life. The initial recognition of Bitcoin is recorded at cost, i.e., the purchase price including transaction fees. But the currency should be impaired on the balance sheet. It means that if its market value drops below its recorded cost on the balance sheet, the company must write down its value to the lower market price, recognizing a loss. This loss cannot be reversed if the market value rises later, ensuring the asset is not overstated. This approach provides investors and stakeholders with clarity on the company’s exposure to digital assets, reflecting both the potential value and risks inherent in holding Bitcoin as part of the company’s asset base. 
Reshaping Corporate financial metrics
By placing Bitcoin on corporate balance sheets, some big firms in the US acknowledge its role beyond speculation, as a store of value and digital asset akin to traditional financial instruments. Such companies evaluate performance not with traditional key performance indicators like EPS (earnings per share) or EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortisation), but through a Bitcoin-native financial lens, guided by three metrics: 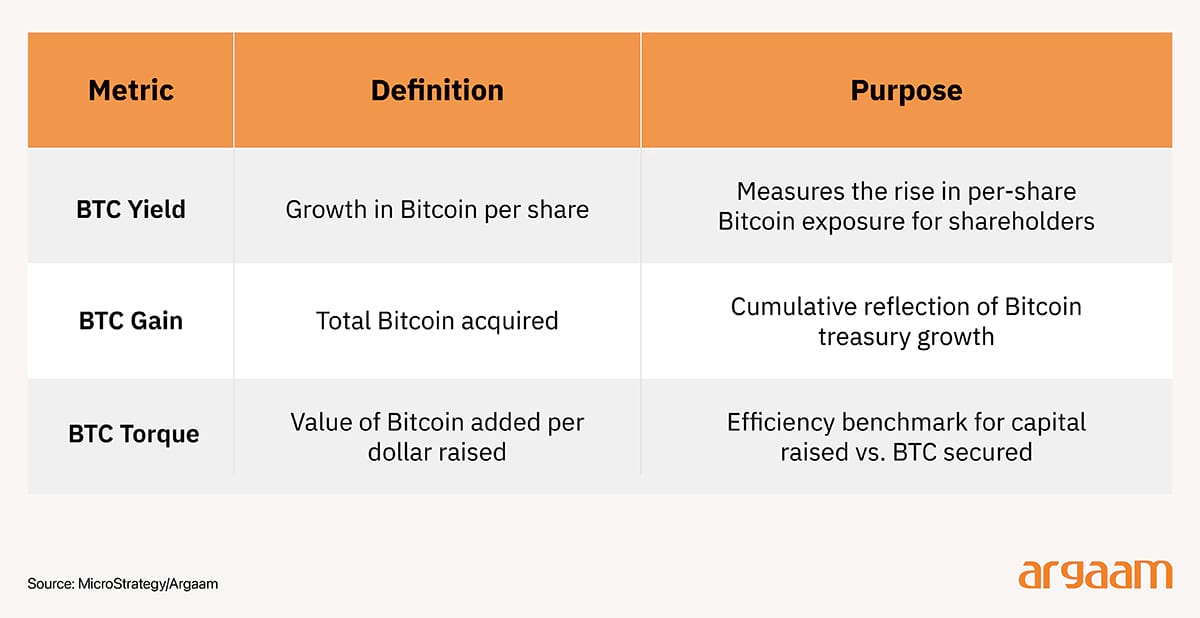 MicroStrategy, a high-tech American firm originally founded in 1989 under the name Strategy, exemplifies a remarkable corporate evolution that underscores its success in leveraging financial innovation and strategic foresight. Its status as the largest corporate holder of bitcoin—with 597,325 bitcoins valued at approximately $64 billion as of June 30, 2025—highlights its pioneering embrace of crypto-centric financial assets. MicroStrategy has played a pioneering role in adopting crypto-centric financial metrics, distinguishing itself as a first-mover among publicly traded companies to integrate cryptocurrency holdings into its financial reporting and strategic framework. This innovative approach reflects the company's recognition of Bitcoin not merely as an investment asset but as a central component of its corporate treasury management and value proposition. This strategic move reflects a forward-thinking approach consistent with findings that early fintech adoption, transparency, and integration of innovative metrics can significantly enhance corporate performance. MicroStrategy's most recent bitcoin purchases were financed through a mix of capital raised via the sale of common stock (MSTR) and newly issued preferred stocks (STRK and STRF --- which are ticker symbols like MSTR on NASDAQ-100) 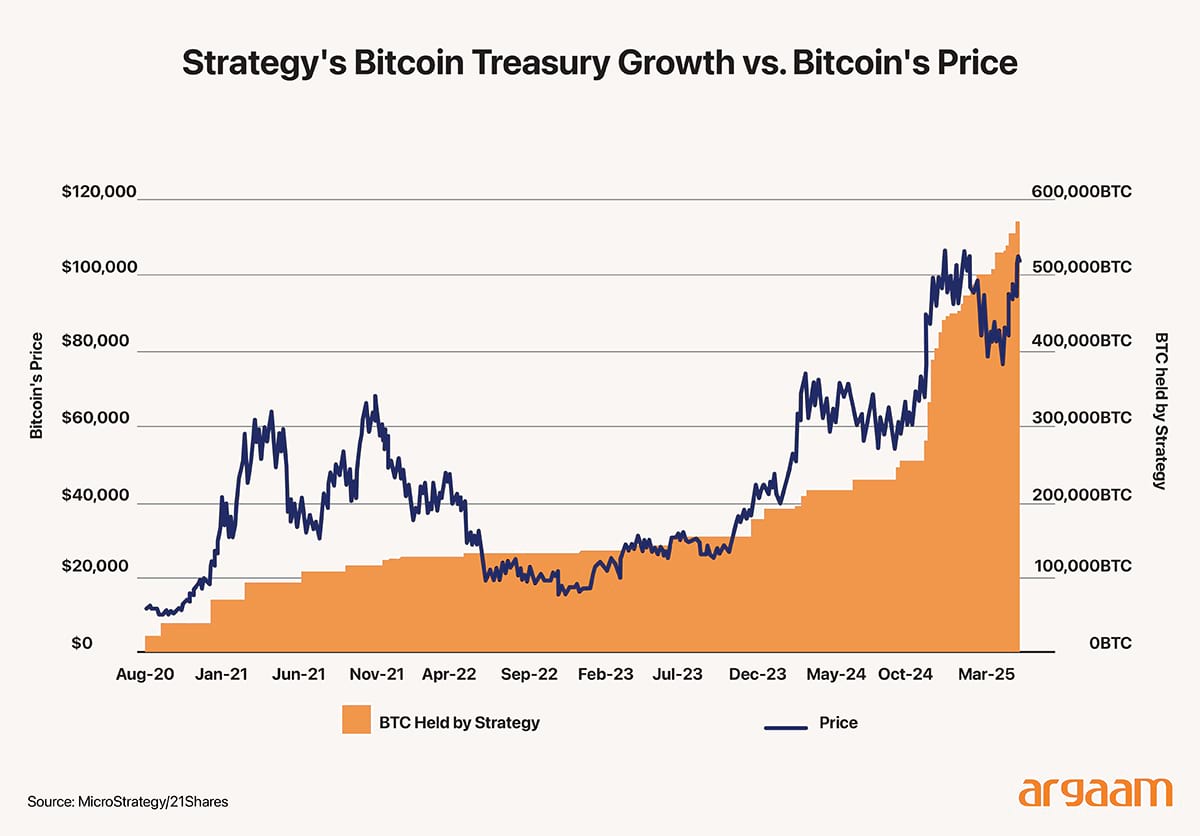 In conclusion, adopting Bitcoin as collateral could provide corporations and financial institutions in Saudi Arabia with access to a new class of digital assets beyond traditional forms like cash or real estate. Leveraging Bitcoin as a security mechanism offers enhanced flexibility and expanded opportunities for businesses to obtain financing and raise capital. This underscores the evolving significance of cryptocurrencies interntionally not only as investment vehicles but also as practical tools that can facilitate borrowing, lending, and the development of innovative capital market solutions. |
|
|
|
|
|